triangular fibrocartilage complex tfcc tear test|tfcc tear mri vs normal : private label Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; TFCC stress test: applying a force across the ulna with . Hebel Autoclaved Aerated Concrete ® (AAC) Masonry (Solid Block, Cored Block and U-Block) .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Materials for AAC Block Production. AAC is created by a unique manufacturing process that involves the use of natural raw materials and aeration. The key components of AAC typically include sand, cement, lime, .
Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made .
Create Personal Test Create Group Test Enter Test Code . Triangular Fibrocartilage Compl.
Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; . Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign.Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; TFCC stress test: applying a force across the ulna with .The TFCC Compression Test is a common orthopedic test to assess the integrity of the triangular fibrocartilage complex in the wrist.
where is the tfcc located
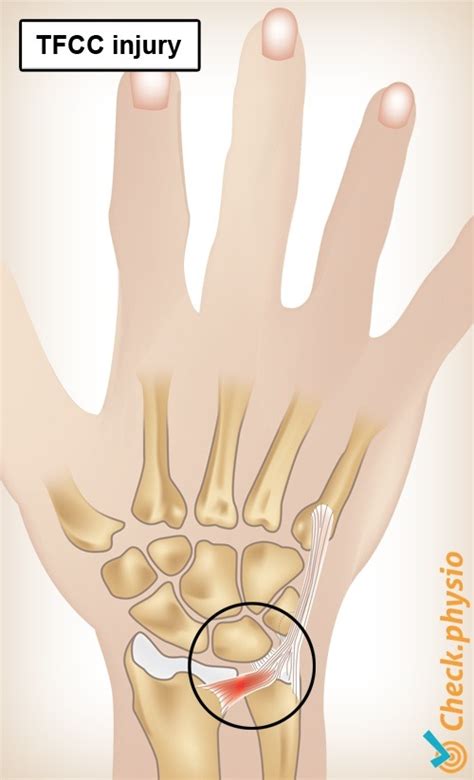
What is a TFCC tear? The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is an area between your radius and ulna, the two main bones that make up your forearm. Your TFCC is made of several.
Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears can cause pain and instability in your wrist. Simple treatments, such as rest and physical therapy, are often enough to heal a TFCC tear. Surgery may be necessary to repair more severe tears.The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a well defined anatomical entity located on the ulnar aspect of the wrist joint functioning primarily to stabilize the distal radio –ulnar joint (DRUJ) and also to act as a shock absorber across the ulno-carpal joint.
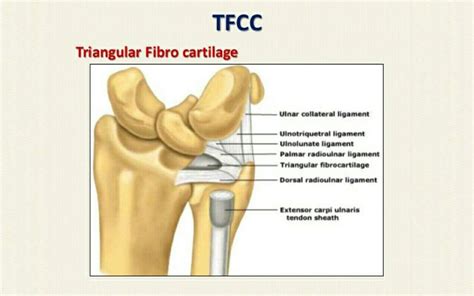
The Triangular FibroCartilage Complex, or TFCC, is an important structure in the wrist. The TFCC is made of tough fibrous tissue and cartilage. This tissue supports the joints between the end of the forearm bones (radius and ulna), adding to their stability.The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), which spans the space between the distal ulna and ulnar carpus, consists of a relatively avascular cartilaginous articular disc (TFC) merged with highly vascularized, ligamentous structures of somewhat variable form.
what does tfcc tear mean
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a load-bearing structure between the lunate, triquetrum, and ulnar head. The function of the TFCC is to act as a stabilizer for the ulnar aspect of the wrist. The TFCC is at risk for either acute or chronic degenerative injury.
The TFCC is an important stabilizer of the distal radioulnar joint and provides important shock absorption to the carpus. The components of the TFCC include: The articular disc. The dorsal and volar radioulnar ligaments. The meniscus homologue. The extensor carpi ulnaris tendon sheath. The ulnocarpal ligaments. Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC) Injuries, a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain, may result from trauma or due to degenerative changes. Diagnosis is made clinically with ulnar sided wrist pain that is worse with ulnar deviation and a positive "fovea" sign.Several physical exam tests can suggest the diagnosis of TFCC injury. These include: TFCC compression test: forearm in the neutral position with ulnar deviation reproduces symptoms; TFCC stress test: applying a force across the ulna with .The TFCC Compression Test is a common orthopedic test to assess the integrity of the triangular fibrocartilage complex in the wrist.
triangular fibrocartilage tear surgery
What is a TFCC tear? The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is an area between your radius and ulna, the two main bones that make up your forearm. Your TFCC is made of several.Triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) tears can cause pain and instability in your wrist. Simple treatments, such as rest and physical therapy, are often enough to heal a TFCC tear. Surgery may be necessary to repair more severe tears.
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a well defined anatomical entity located on the ulnar aspect of the wrist joint functioning primarily to stabilize the distal radio –ulnar joint (DRUJ) and also to act as a shock absorber across the ulno-carpal joint.The Triangular FibroCartilage Complex, or TFCC, is an important structure in the wrist. The TFCC is made of tough fibrous tissue and cartilage. This tissue supports the joints between the end of the forearm bones (radius and ulna), adding to their stability.
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), which spans the space between the distal ulna and ulnar carpus, consists of a relatively avascular cartilaginous articular disc (TFC) merged with highly vascularized, ligamentous structures of somewhat variable form.
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a load-bearing structure between the lunate, triquetrum, and ulnar head. The function of the TFCC is to act as a stabilizer for the ulnar aspect of the wrist. The TFCC is at risk for either acute or chronic degenerative injury.
triangular fibrocartilage complex tear repair
triangular fibro complex cartilage tear
tfcc tear treatment protocol
If you are looking to build a concrete home, one of the many concrete construction systems you can consider using is autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC blocks). In fact, this is one of our top recommendations overall, since .
triangular fibrocartilage complex tfcc tear test|tfcc tear mri vs normal